Check out our recent updates
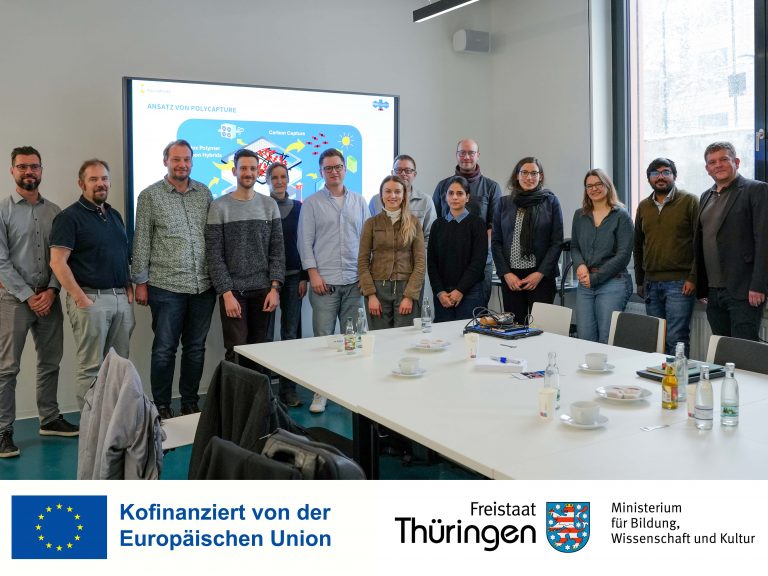

Kick-off for the PolyCapture research group
On Monday, 16 February 2026, the official kick-off meeting of the PolyCapture research group took place at HIPOLE Jena. The participating group leaders and researchers, as well as representatives of…

In cooperation with partners from the DFG Collaborative Research Center TRR 234, CataLight, researchers from HIPOLE Jena have published an article in Nature Communications.

Great discussions and renewed optimism at Batterieforum Deutschland
The annual Batterieforum Deutschland once again brought together policymakers, industry representatives, and researchers on 20 January 2026 to discuss key developments in battery technology. Our colleague Dr. Felix Nagler represented…
Job offers
-
Postdoc (m/f/d) for Supercapacitive Swing Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide at HIPOLE Jena
-
Postdoc (m/f/d) Computational Chemist MOST at HIPOLE Jena
-
Talents Community – Postdoc, PhD Student (f/m/d) for Polymers in Energy Applications at HIPOLE Jena
-
Talents Community – Technician (m/f/d) at HIPOLE Jena
-
Chemistry Internship opportunities for school and university students
The central strategic goal of HIPOLE Jena is the accelerated, knowledge-based development of sustainable polymer materials for scalable energy technologies.
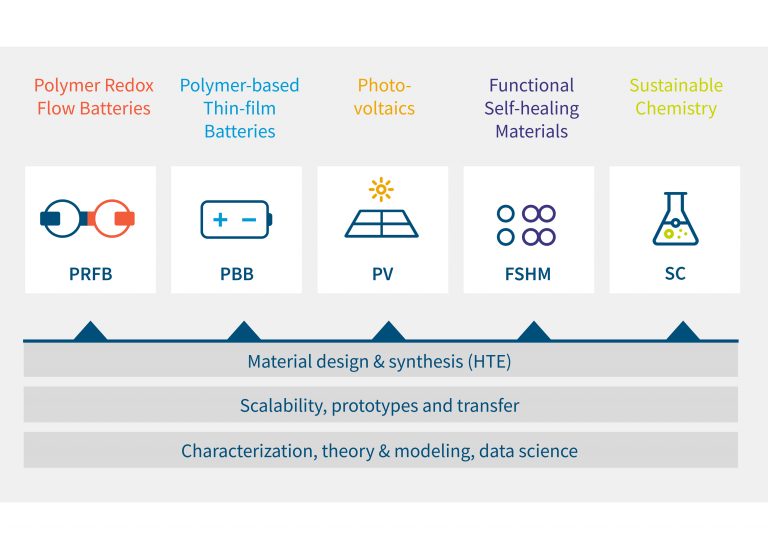
HIPOLE Jena is based on three research pillars:
- Material design & synthesis
- Scalability, prototypes, and transfer
- Characterization, theory & modeling and data science
This triad forms the basis for 5 areas of the HIPOLE Jena research mission:
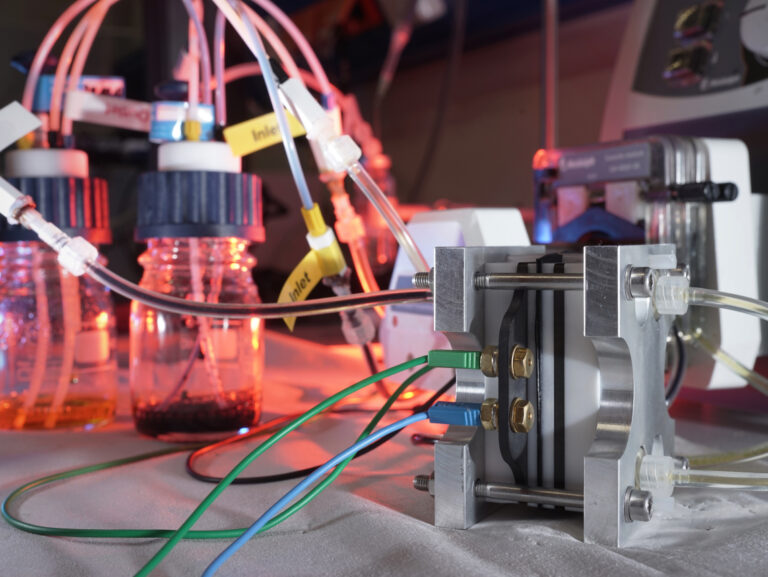
Polymer redox-flow batteries
Redox-flow batteries (RFB) are a special battery technology. In contrast to many other battery systems, with RFB the performance and capacity can be scaled independently of each other. RFBs are particularly interesting for stationary energy storage. As part of HIPOLE Jena, organic, polymer-based electrolytes are being investigated, which makes the use of critical metals/metal ions in the electrolytes obsolete.
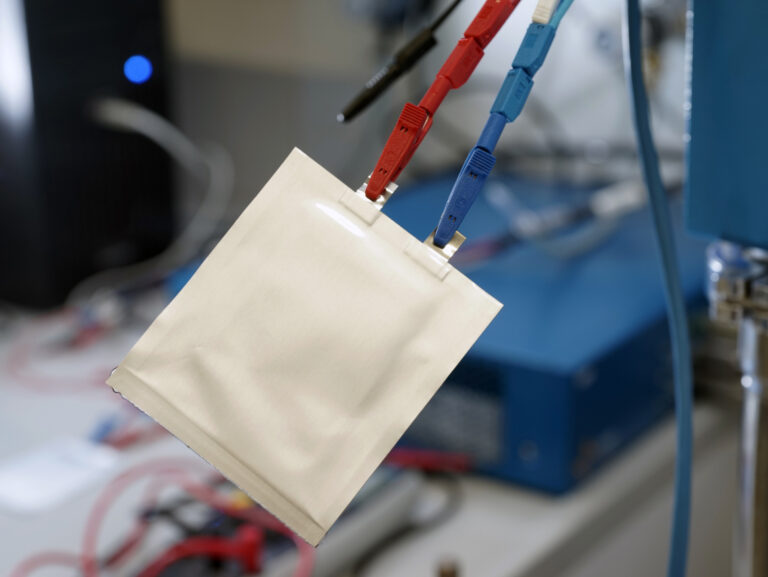
Polymer-based thin-film batteries
The large area of organic electronics opens up many new application possibilities, such as in the area of smart textiles or the “Internet of Things”. In this context, polymer-based active materials and electrolytes allow the printing production of flexible, tailor-made batteries. In HIPOLE Jena, the next generation of these materials is being investigated, which should, for example, enable a longer lifespan.
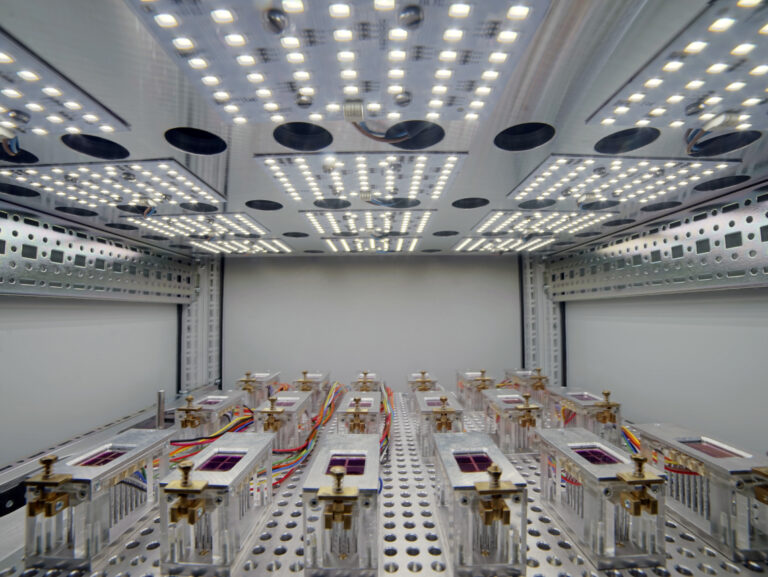

Photovoltaics
Commercial photovoltaic technologies have reached the terawatt (TW) range in terms of installed capacity worldwide. There will continue to be a very high demand for photovoltaic systems in the next few years, requiring scalable technologies to meet the ever-growing demand. HIPOLE Jena is dedicated to perovskite solar cells. The use of polymers is intended to improve stability, for example.
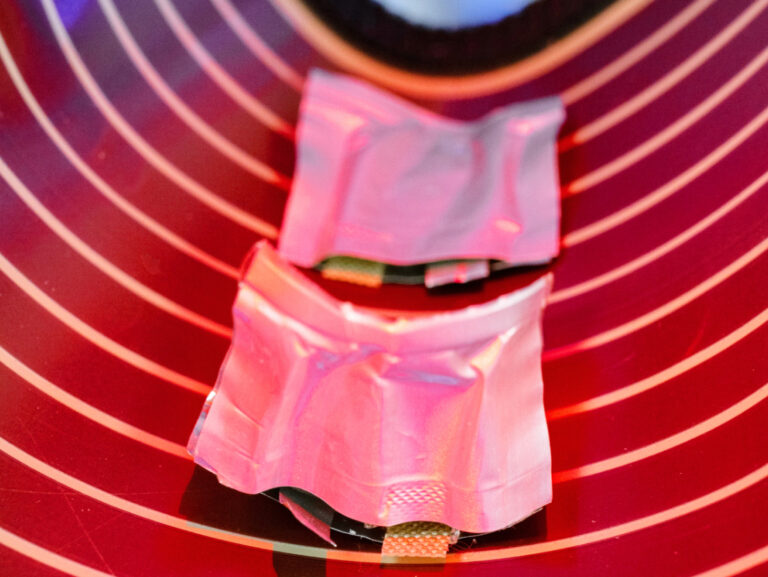

Functional self-healing materials
Functional self-healing materials represent a special field of research. These can restore their original properties after damage. For example, in battery electrodes, the conductivity should be restored after damage to the electrode. Comparable approaches should also be used for solar cells.
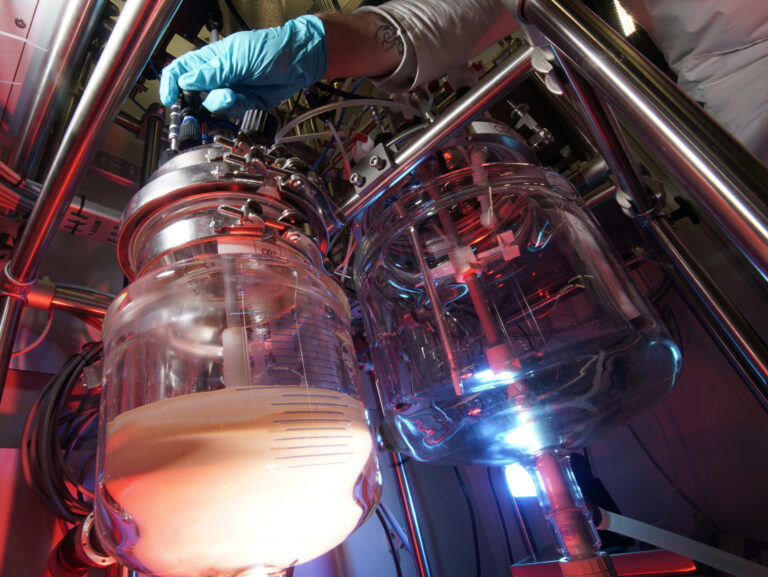

Sustainable chemistry
In the plastic age, which is also strongly associated with the negative environmental impacts of plastics (e.g. microplastics), sustainability plays an important role. Therefore, the polymers for the various applications should be created based on sustainable resources and their recycling should be possible. For example, the use of CO2 as a building block for polymers plays an important role.

